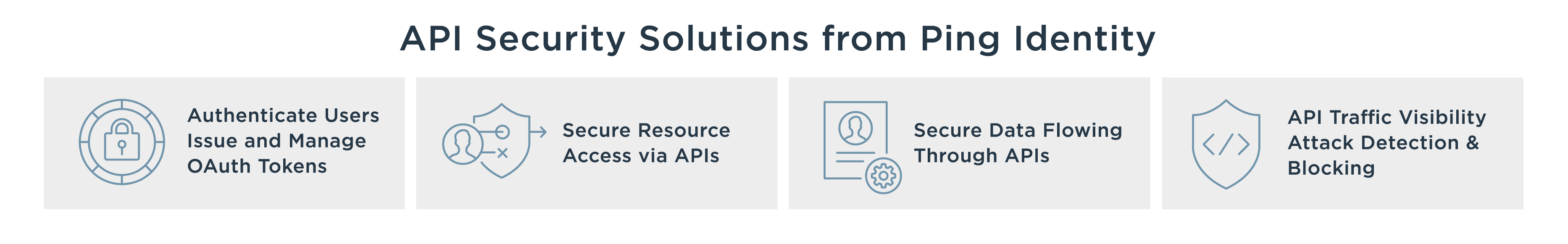
What is API Security?
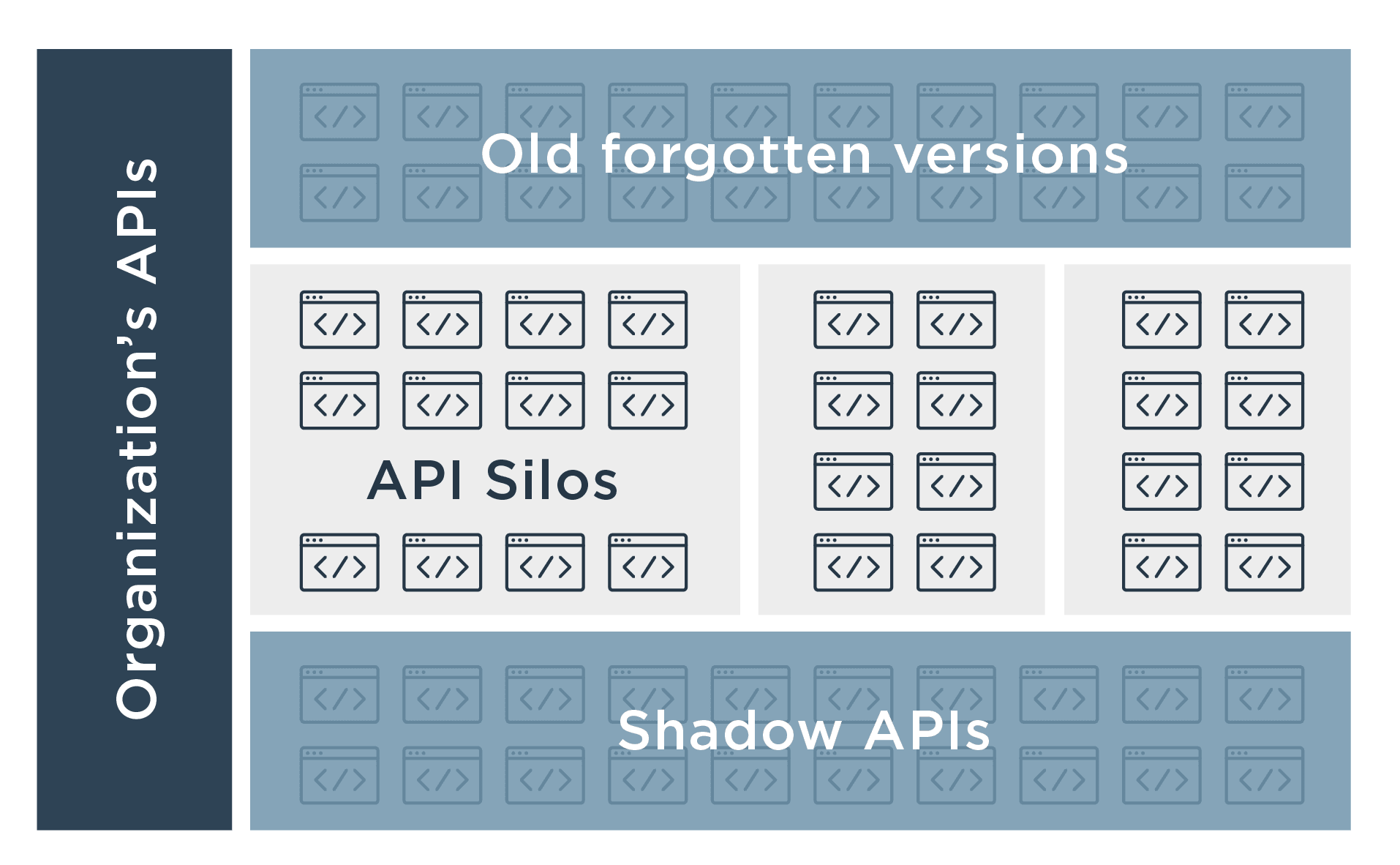
Web API security is the application of any security best practice applied to web APIs, which are prevalent in modern applications. Web API security includes API access control and privacy, as well as the detection and remediation of attacks on APIs through API reverse engineering and the exploitation of API vulnerabilities as described in OWASP API Security Top 10.
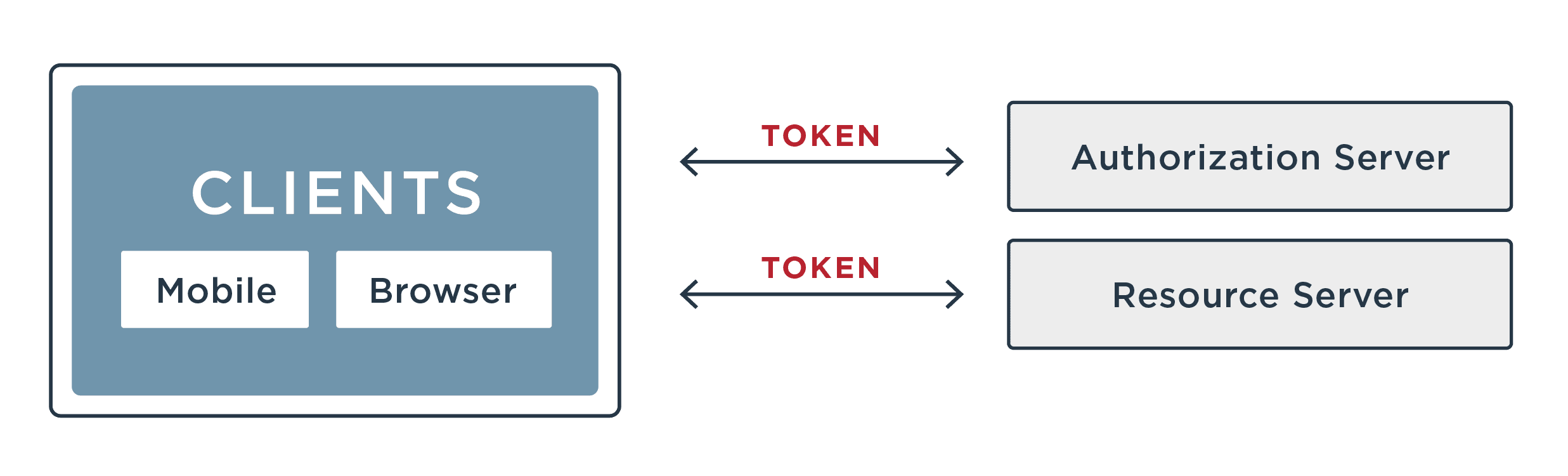
Whether an application is targeting consumers, employees, partners or otherwise, the client-side of an application (e.g., a mobile app, a web app) interacts with the server-side of an application via an Application Programming Interface (API). Simply put, APIs make it easy for a developer to create a client-side app. Microservice architectures are also made possible by APIs.
While this access is invaluable for your employees, partners, and customers, it also makes APIs attractive targets for hackers and rogue insiders.
A growing number of highly publicized attacks have revealed how vulnerable APIs can be to attack vectors like credential stuffing, stolen tokens, data extraction, broken authentication, account takeover, and breaches through a partner.
Existing API security solutions like content delivery networks and application delivery controllers, web application firewalls, identity and access management systems, and API gateways provide basic protections for your API infrastructure against volumetric DDOS attacks, OWASP top ten vulnerabilities, session hijacking, and invalid input attacks, to name a few.
But they're not enough to stop hackers determined to exploit vulnerabilities unique to each API.
To learn more about four common gaps in API security, visit our website at the link below or visit the API intelligence page at www.pingidentity.com.
Thanks for watching.
Because they’re often available over public networks (access from anywhere), APIs are typically well documented or easily reverse-engineered. Also highly sensitive to denial of service (DDOS) type incidents, APIs are attractive targets for bad actors.
An attack might include bypassing the client-side application in an attempt to disrupt the functioning of an application for other users or to breach private information. API security is focused on securing this application layer and addressing what can happen if a malicious hacker were to interact with the API directly.